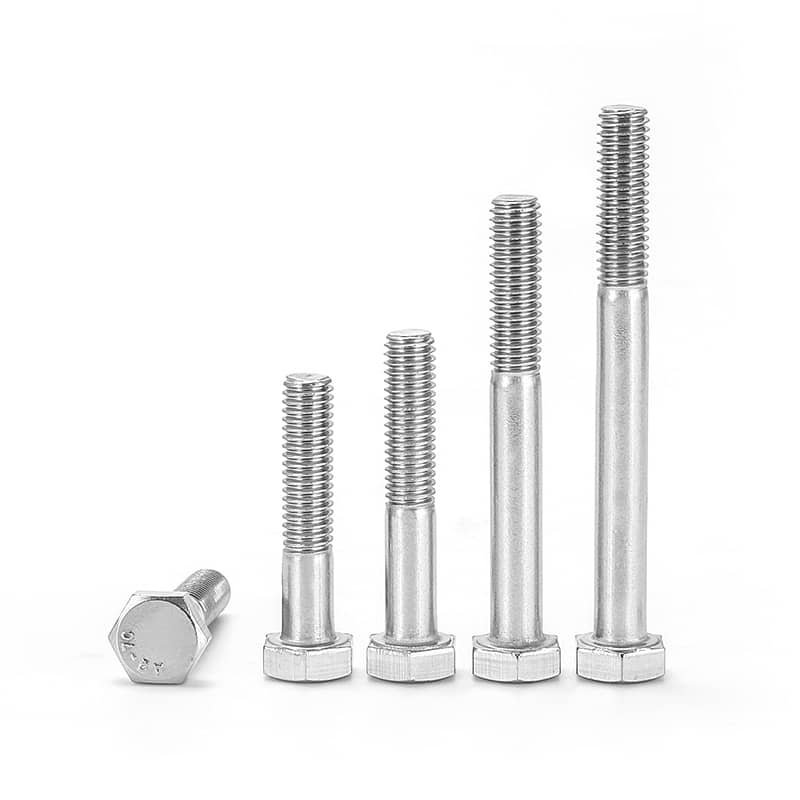
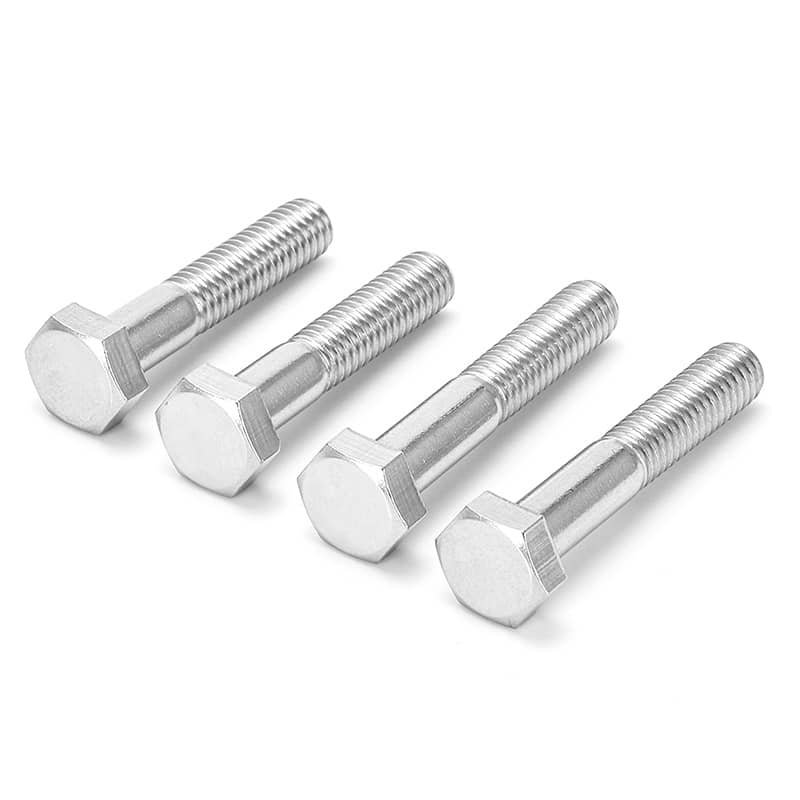
DIN931 Hex Head Bolts Half Thread A2-70 Stainless Steel 304
DIN 931: A Comprehensive Guide to Hexagon Head Bolts
When it comes to fastening systems in engineering and construction, bolts play an essential role. Among the various types of bolts, DIN 931 stands out as a commonly used standard for hexagon head bolts. Whether you’re an engineer, a DIY enthusiast, or a professional in the construction industry, understanding the specifics of DIN 931 is critical for choosing the right fasteners for your projects.
This article will explore DIN 931 in detail, explaining its characteristics, applications, specifications, and how it compares to other similar standards. We’ll also delve into material selection, corrosion resistance, and the factors to consider when selecting DIN 931 bolts for different tasks.
1. What Is DIN 931?
DIN 931 refers to a specific standard of hexagon head bolts, primarily defined by the German Institute for Standardization (Deutsches Institut für Normung). The standard outlines the dimensions, tolerances, and material properties of bolts used in a wide variety of applications.
These bolts are typically characterized by their six-sided hexagonal head, which is designed to be turned using a wrench or socket.
The DIN 931 standard applies specifically to bolts with a partial thread, meaning that the threading does not run the entire length of the bolt. This makes them ideal for applications where the bolt needs to anchor securely into a material without the full thread extending into the fastened material.
2. Key Features of DIN 931 Hexagon Head Bolts
DIN 931 bolts are part of a larger family of hexagon head bolts, but they differ in a few key areas:
- Head Shape: As the name suggests, DIN 931 bolts have a hexagonal head that provides a high level of torque when tightened. This design makes it easier to apply higher forces and is ideal for heavy-duty applications.
- Partial Threading: The main distinguishing feature of DIN 931 bolts is the partial threading. In contrast to fully threaded bolts like DIN 933, the partial thread only extends for part of the bolt’s length. This feature makes them more suitable for applications where the fastening load is primarily carried by the unthreaded portion of the bolt.
- Material: DIN 931 bolts are typically made from high-strength steel, although they can also be made from stainless steel, brass, or other corrosion-resistant materials. The specific material choice depends on the application and environment where the bolt will be used.
- Strength: These bolts are designed to withstand high levels of stress and torque. The standard specifies a minimum tensile strength and yield strength for the materials used, ensuring that they can endure heavy loads without failure.
- Thread Pitch and Diameter: DIN 931 bolts come in a variety of diameters and thread pitches, making them versatile for different applications. The diameter ranges from M6 (6mm) to M30 (30mm) or larger, with different thread pitches available depending on the bolt’s size.
3. Applications of DIN 931 Hexagon Head Bolts
Due to their robustness and versatility, DIN 931 bolts are used in a wide range of industries and applications. Some of the most common applications include:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, bolts are used extensively to assemble parts and components, from engines to chassis. DIN 931 bolts, with their high tensile strength, are particularly suited for critical automotive applications, including engine blocks, suspension systems, and transmission parts.
Construction and Civil Engineering
In construction and civil engineering projects, bolts are essential for securing structural components like steel beams, concrete panels, and heavy equipment. The partial threading of DIN 931 bolts makes them ideal for fastening applications where the bolt does not need to penetrate completely through the material but still requires a strong connection.
Machine Building
Machines and industrial equipment require fasteners that can hold large parts together under significant strain. DIN 931 bolts are commonly used in machine building for components such as motors, pumps, and compressors. Their ability to withstand high loads makes them an excellent choice for these demanding environments.
Railway and Infrastructure
The railway industry uses a variety of fasteners, and DIN 931 bolts are a key component. These bolts are used in the construction of rail track systems, bridges, and tunnels, where safety and load-bearing capacity are paramount.
Aerospace
In aerospace, DIN 931 bolts are used in the construction of aircraft, satellites, and other high-performance systems. The combination of strength and reliability makes them a natural choice for applications that require precision and durability.
4. DIN 931 vs. DIN 933: What’s the Difference?
The primary difference between DIN 931 and DIN 933 bolts lies in the threading. As previously mentioned, DIN 931 bolts have partial threading, while DIN 933 bolts are fully threaded along their entire length.
Partial Threading (DIN 931)
- The thread extends only partially along the length of the bolt.
- The unthreaded section of the bolt is typically embedded in the material being fastened, ensuring a tight and secure hold.
- Often used where the primary load-bearing is on the shank or the unthreaded portion.
Full Threading (DIN 933)
- The thread extends the entire length of the bolt.
- This design allows the bolt to engage more material, increasing its holding power.
- Typically used in applications where the bolt must be threaded all the way into a nut or tapped hole.
5. Material Selection for DIN 931 Bolts
The material selection for DIN 931 bolts is critical to their performance in various environments. The standard does not prescribe a specific material but provides guidelines for selecting materials based on the intended application.
Carbon Steel
The most common material for DIN 931 bolts is carbon steel, particularly in grades such as 8.8, 10.9, and 12.9. These grades refer to the tensile strength of the bolt (in MPa), with 8.8 bolts being the most common. Carbon steel bolts are suitable for general-purpose applications and offer good strength and durability at an affordable price.
Stainless Steel
For applications where corrosion resistance is essential, stainless steel bolts (such as A2 or A4 stainless steel) are often used. These bolts provide superior resistance to rust and corrosion, making them ideal for outdoor and marine environments, as well as in food processing and pharmaceutical industries.
Alloy Steel
In applications that demand even higher strength, alloy steel bolts can be used. These bolts are typically used in heavy-duty environments, such as construction machinery or oil and gas infrastructure.
Brass and Other Materials
In some niche applications, such as in electrical components or where non-magnetic properties are required, brass or other materials may be used for DIN 931 bolts. However, these materials are less common than carbon and stainless steel.
6. Corrosion Resistance and Coatings
Bolts are often exposed to harsh environments, including moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. As such, corrosion resistance is a critical factor to consider when selecting a DIN 931 bolt. There are several methods used to protect bolts from corrosion:
- Galvanization: The bolt is coated with a thin layer of zinc to provide corrosion resistance. Galvanized bolts are commonly used in outdoor and marine environments.
- Black Oxide Coating: This coating provides mild corrosion resistance and a dark finish, commonly seen in automotive and industrial applications.
- Phosphate Coating: Often used in automotive and machinery applications, phosphate coatings enhance corrosion resistance and improve the bolt’s ability to resist wear and tear.
- Stainless Steel: Stainless steel bolts are inherently resistant to rust and corrosion, making them ideal for environments with high humidity or exposure to chemicals.
- Nickel Plating: Nickel plating offers good corrosion resistance and is often used in situations requiring a combination of strength and aesthetic appeal.
7. Key Considerations When Choosing DIN 931 Bolts
When selecting DIN 931 bolts for a particular application, several factors must be taken into account to ensure the correct choice:
- Load-Bearing Requirements: Consider the amount of force the bolt needs to withstand. Higher-strength bolts (such as grade 10.9 or 12.9) may be necessary for heavy-duty applications.
- Corrosion Resistance: Select the material or coating based on the environmental conditions the bolt will be exposed to, such as humidity, temperature, or chemicals.
- Bolt Size: The size and diameter of the bolt must match the application requirements. Larger bolts are suitable for high-stress applications, while smaller bolts are used in light-duty tasks.
- Thread Pitch: The thread pitch refers to the distance between threads on the bolt. Ensure that the pitch matches the nut or tapped hole being used to secure the bolt.
- Tightening Method: Depending on the application, you may need a bolt that can be tightened with a standard wrench, a torque wrench, or a special tool designed for heavy-duty fastening.
8. Conclusion: The Versatility and Reliability of DIN 931 Bolts
DIN 931 bolts are a vital component in a wide array of industries due to their strength, durability, and versatility. With their partial threading design, they offer a secure fastening solution for applications where full thread engagement is unnecessary. The choice of materials and coatings further expands their usefulness in diverse environments, from construction sites to aerospace.
By understanding the specifications, applications, and selection criteria for DIN 931 bolts, engineers and professionals can ensure that they are using the right fasteners for the job, contributing to the safety, reliability, and longevity of their projects. As industries continue to innovate and evolve, the role of fasteners like DIN 931 bolts will remain crucial in holding together the world’s infrastructure and technology.
Description:
Product Name: | Hex Head Bolts Half Thread |
Specification: | DIN931 |
Material Grade: | Stainless Steel 304(A2-70) |
Measurement: | Metric(MM) |
Diameter Range: | M6,M8,M10,M12,M14,M16,M20,M22,M24,M27,M30,M33 |
Length Range: | 30mm, 35mm, 40mm, 45mm, 50mm, 55mm, 60mm, 65mm, 70mm, 75mm, 80mm, 85mm, 90mm, 95mm, 100mm, 105mm, 110mm, 115mm, 120mm, 125mm, 130mm, 135mm, 140mm, 145mm, 150mm, 160mm, 165mm, 170mm, 175mm, 180mm, 190mm, 200mm, 210mm, 220mm, 230mm, 240mm, 250mm, 310mm |
Surface Finish: | Plain |
Color: | Silvery |
Place of Origin: | DongGuan, China |
Quality Control: | 100% inspection during production |
Packaging: | Plastic bags/cartons |
Sample: | Availbale |
Customized: | Availbale |
Screw Size Conversion Chart:
Screw Size | Diameter(mm) | Diameter(inch) | Nearest Fraction(inch) |
#0 | 1.52 | 0.060 | 1/16 |
#1 | 1.85 | 0.073 | 5/64 |
#2 | 2.18 | 0.086 | 3/32 |
#3 | 2.51 | 0.099 | 7/64 |
#4 | 2.84 | 0.112 | 7/64 |
#5 | 3.18 | 0.125 | 1/8 |
#6 | 3.51 | 0.138 | 9/64 |
#8 | 4.17 | 0.164 | 5/32 |
#10 | 4.83 | 0.190 | 3/16 |
#12 | 5.49 | 0.216 | 7/32 |
#14 | 6.35 | 0.250 | 1/4 |
Drawing:
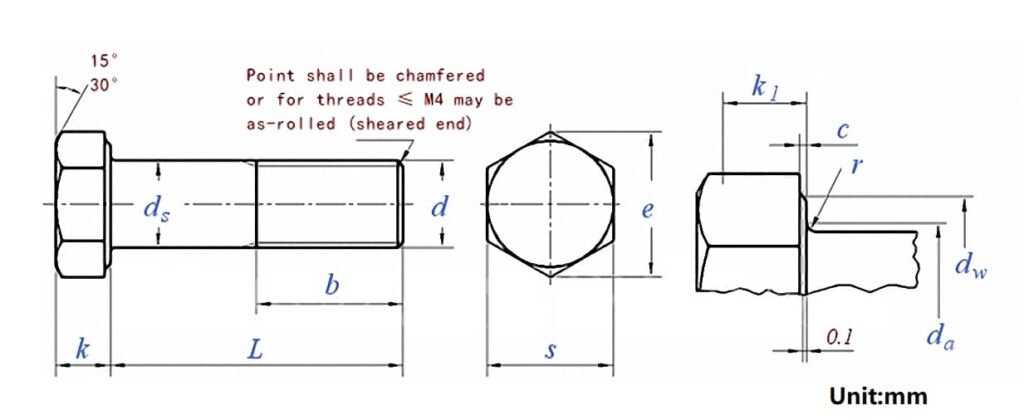
Data Sheet:
Thread Size | M1.6 | M2 | M2.5 | M3 | M3.5 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M10 | M12 |
P | 0.35 | 0.4 | 0.45 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 1.25 | 1.5 | 1.75 |
b (L≤125) | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 26 | 30 |
b (125<L≤200) | - | - | - | - | - | - | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 32 | 36 |
b (L>200) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 45 | 49 |
c (min) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
c (max) | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
da (max) | 2 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 5.7 | 6.8 | 7.8 | 9.2 | 11.2 | 13.7 |
ds max= nominal size | 1.6 | 2 | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 |
ds- Grade A (min) | 1.46 | 1.86 | 2.36 | 2.86 | 3.32 | 3.82 | 4.82 | 5.82 | 6.78 | 7.78 | 9.78 | 11.73 |
ds- Grade B (min) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
dw- Grade A (min) | 2.4 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 4.6 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 6.9 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 11.6 | 15.6 | 17.4 |
dw- Grade B (min) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
e- Grade A (min) | 3.41 | 4.32 | 5.46 | 6.01 | 6.58 | 7.66 | 8.79 | 11.05 | 12.12 | 14.38 | 18.9 | 21.1 |
e- Grade B (min) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
k- (Nominal Size) | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 2 | 2.4 | 2.8 | 3.5 | 4 | 4.8 | 5.3 | 6.4 | 7.5 |
k- Grade A (min) | 0.98 | 1.28 | 1.58 | 1.88 | 2.28 | 2.68 | 3.35 | 3.85 | 4.65 | 5.15 | 6.22 | 7.32 |
k- Grade A (max) | 1.22 | 1.52 | 1.82 | 2.12 | 2.52 | 2.92 | 3.65 | 4.15 | 4.95 | 5.45 | 6.56 | 7.68 |
k- Grade B (min) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
k- Grade B (max) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
k1 (min) | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.28 | 2.63 | 3.19 | 3.54 | 4.28 | 5.05 |
r (min) | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
s max= nominal size | 3.2 | 4 | 5 | 5.5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 17 | 19 |
s- Grade A (min) | 3.02 | 3.82 | 4.82 | 5.32 | 5.82 | 6.78 | 7.78 | 9.78 | 10.73 | 12.73 | 16.73 | 18.67 |
s- Grade B (min) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Thread Size | M14 | M16 | M18 | M20 | M22 | M24 | M27 | M30 | M33 | M36 | M39 |
P | 2 | 2 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3 | 3 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 4 | 4 |
b(L≤125) | 34 | 38 | 42 | 46 | 50 | 54 | 60 | 66 | 72 | 78 | 84 |
b(125<L≤200) | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 66 | 72 | 78 | 84 | 90 |
b(L>200) | 53 | 57 | 61 | 65 | 69 | 73 | 79 | 85 | 91 | 97 | 103 |
c (min) | 0.15 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
c (max) | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1 |
da (max) | 15.7 | 17.7 | 20.2 | 22.4 | 24.4 | 26.4 | 30.4 | 33.4 | 36.4 | 39.4 | 42.4 |
ds max= nominal size | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 | 39 |
ds- Grade A (min) | 13.73 | 15.73 | 17.73 | 19.67 | 21.67 | 23.67 | - | - | - | - | - |
ds- Grade B (min) | - | 15.57 | 17.57 | 19.48 | 21.48 | 23.48 | 26.48 | 29.48 | 32.38 | 35.38 | 38.38 |
dw- Grade A (min) | 20.5 | 22.5 | 25.3 | 28.2 | 30 | 33.6 | - | - | - | - | - |
dw- Grade B (min) | - | 22 | 24.8 | 27.7 | 29.5 | 33.2 | 38 | 42.7 | 46.5 | 51.1 | 55.9 |
e- Grade A (min) | 24.49 | 26.75 | 30.14 | 33.53 | 35.72 | 39.98 | - | - | - | - | - |
e- Grade B (min) | - | 26.17 | 29.56 | 32.95 | 35.03 | 39.55 | 45.2 | 50.85 | 55.37 | 60.79 | 66.44 |
k- (Nominal Size) | 8.8 | 10 | 11.5 | 12.5 | 14 | 15 | 17 | 18.7 | 21 | 22.5 | 25 |
k- Grade A (min) | 8.62 | 9.82 | 11.28 | 12.28 | 13.78 | 14.78 | - | - | - | - | - |
k- Grade A (max) | 8.98 | 10.18 | 11.72 | 12.72 | 14.22 | 15.22 | - | - | - | - | - |
k- Grade B (min) | - | 9.71 | 11.15 | 12.15 | 13.65 | 14.65 | 16.65 | 18.28 | 20.58 | 22.08 | 24.58 |
k- Grade B (max) | - | 10.29 | 11.85 | 12.85 | 14.35 | 15.35 | 17.35 | 19.12 | 21.42 | 22.92 | 25.42 |
k1 (min) | 5.96 | 6.8 | 7.8 | 8.5 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 11.7 | 12.8 | 14.4 | 15.5 | 17.2 |
r (min) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
s max= nominal size | 22 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 32 | 36 | 41 | 46 | 50 | 55 | 60 |
s- Grade A (min) | 21.67 | 23.67 | 26.67 | 29.67 | 31.61 | 35.38 | - | - | - | - | - |
s- Grade B (min) | - | 23.16 | 26.15 | 29.16 | 31 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 49 | 53.8 | 58.8 |
Common Imperial to Metric Equivalent Chart:
Imperial(inch) | Metric(mm) | Imperial(inch) | Metric(mm) | |
1/16 | 1.59 | 1-3/8 | 34.93 | |
1/8 | 3.18 | 1-1/2 | 38.10 | |
3/16 | 4.76 | 1-5/8 | 41.28 | |
1/4 | 6.35 | 1-3/4 | 44.45 | |
5/16 | 7.94 | 1-7/8 | 47.63 | |
3/8 | 9.53 | 2 | 50.80 | |
7/16 | 11.11 | 2-1/4 | 57.15 | |
1/2 | 12.70 | 2-1/2 | 63.50 | |
9/16 | 14.29 | 2-3/4 | 69.85 | |
5/8 | 15.88 | 3 | 76.20 | |
11/16 | 17.46 | 3-1/4 | 82.55 | |
3/4 | 19.05 | 3-1/2 | 88.90 | |
7/8 | 22.23 | 3-3/4 | 95.25 | |
1 | 25.40 | 4 | 101.60 | |
1-1/4 | 31.75 |
Equivalent Norm:
GB | ISO | DIN | EN | UNI | NF | IS |
GB /T 5782 | ISO 4014 | DIN EN ISO 4014 | EN 24014 | UNI 5734 | NF E 25-112 | IS 1364(-1) |
Some of the above standards may be approximate equivalents; in case of disagreement, the original standard shall prevail. | ||||||
Related products
-

Self drilling Screws Phillips Flat Head DIN7504O Stainless Steel 410
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Self drilling Screws Hex Washer Head DIN7504K Stainless Steel 304
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Bolts Hex Flange DIN6921 Class 8.8 Carbon Steel 10B21 Black
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page -

Bolts Hex Flange Fully Threaded DIN6921 Class 8.8 Carbon Steel 10B21
Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page